Big Data definition
The term big Data refers to a volume of data that exceeded the capabilities of the software commonly used to view capturing, administering, and processing data.
As the computing capacity is getting higher and the number from which is considered a dataset as big data is increasing, in 2012 already fixed the border in 12 terabytes.
All this would not have been possible if not for Hadoop, a system that allows to implement on hardware at a relatively low cost, for the analysis of large volumes of data of the three types of existing data (structured, unstructured and Semi-structured).
It is worth mentioning the importance that Spark is acquiring as an evolution of Hadoop.
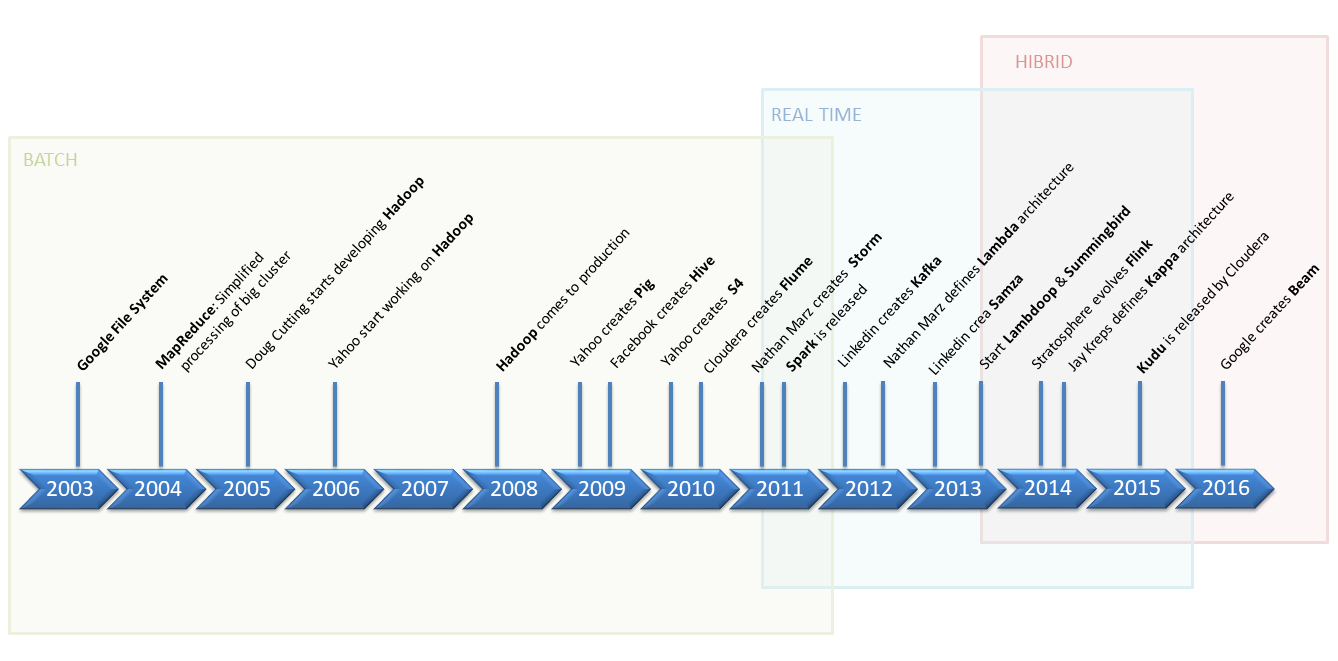
Time evolution of Big data tools
Big Data processing
The processing of large volumes of data is divided into several phases, and each one of them is shown as well as the most important tools for each of them:
Intake
Transformation
Processing
- Map-Reduce, Storm, Samza, IBM InfoSphere, S4, complexion, Spark streaming, Flink,…
Storage
- HDFS, HBase, S3, Kudo, ElasticSearch, Cassandra, MongoDB, MariaDB,…
Display
- Jupyter, Zeppelin, Google Chart, D3. js, Plotty, Kibana, Shiny, Recorda, Loggy, Splunk, Tableau, QLink, Google Cloud Platform, Power Bi,…
Big Data management Platforms
Commercial platforms
- Cloudy
- Hortonworks
- MapR
- Pivotal
Commercial platforms in the cloud
- Amazon Web Service
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- IBM InfoSphere




0 Comments